
Host A receives the frame and sends its MAC address to R1 (ARP reply).If it is not, R1 will send an ARP request to the broadcast MAC address of FF:FF:FF:FF:FF:FF. R1 checks its ARP table to find out whether the Host A’s MAC address is known.

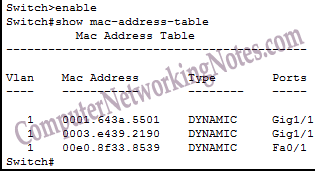
The subnet on which Host A resides is a directly connected subnet. Here are the steps R1 needs to take before forwarding frames to Host A: Interface – the interface on R1 on which the corresponding host is connected.For Ethernet, this value will always be ARPA. Hardware – the MAC address of the host with the corresponding IP address.Each time an entry is used, the age will be reset back to zero. 6 in this column means that the entry was last used 6 minutes ago. Age – by default, an entry will be removed from the ARP table if it wasn’t used in 240 minutes.Address – the IP address associated with the MAC address, in our case the IP address of Host A.Protocol – the protocol type, almost always Internet.Here is a brief description of each field: Consider the entry for Host A: Protocol Address Age (min) Hardware Addr Type Interface The ARP table also lists the MAC addresses of the two connected hosts. The – in the age column indicates that the entry will never be timed out. The ARP table contains two entries for R1’s own two interfaces with the IP address of 10.0.0.1 and 172.16.0.1. Internet 10.0.0.10 6 73 ARPA GigabitEthernet0/0 Protocol Address Age (min) Hardware Addr Type Interface Here is the output of the R1’s ARP table: R1#show ip arp Before exchanging frames with either host, R1 will need to know their MAC addresses. The IP-to-MAC address mapping are kept in the router’s ARP table. Just like regular hosts, if a Cisco router wants to exchange frames with a host in the same subnet, it needs to know its MAC address.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
